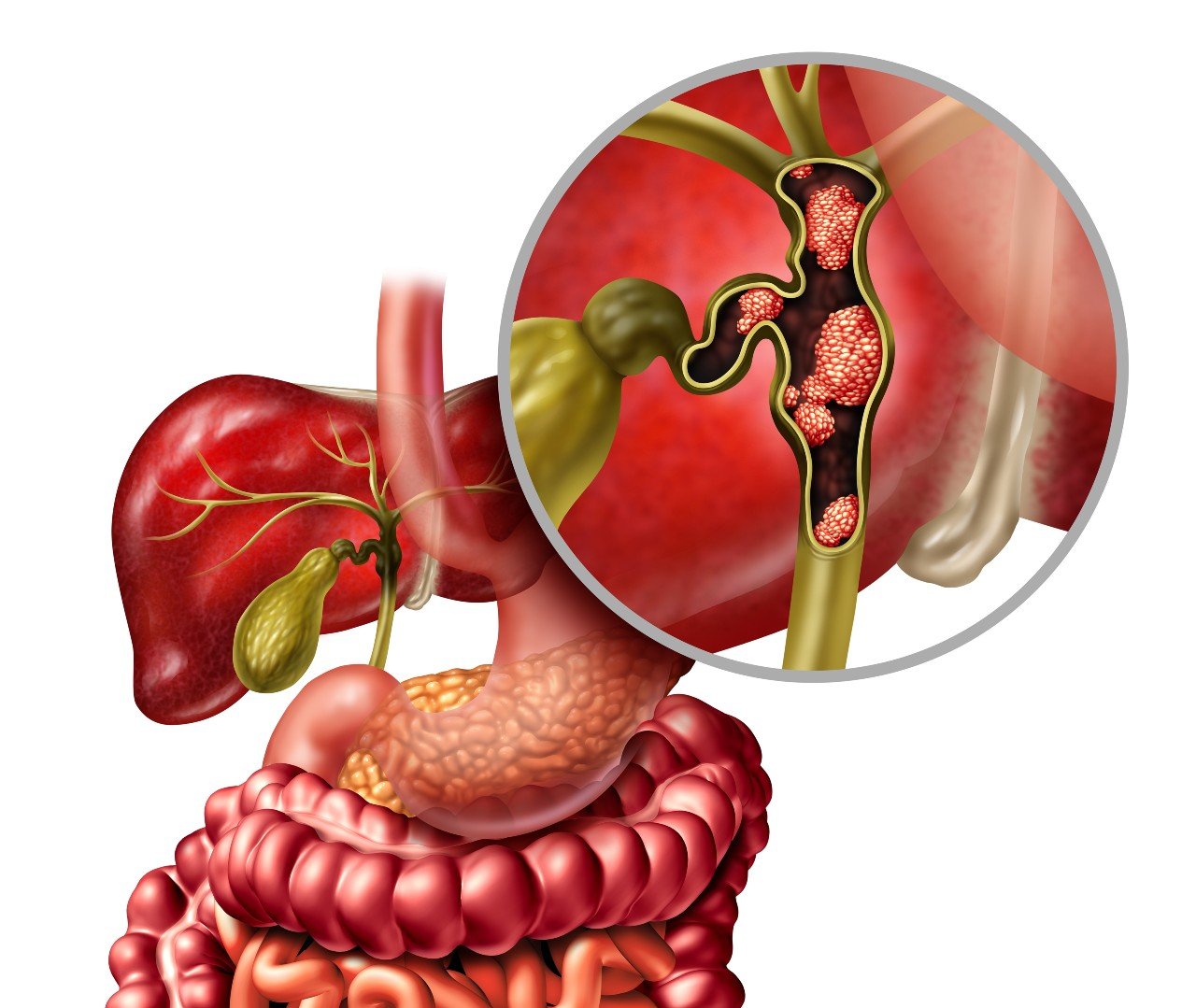
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that originates in the bile ducts.
Types :-
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma :- Originates in the bile ducts inside the liver.
- Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma :- Originates in the bile ducts outside the liver and is further divided into :
- Perihilar (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoma :- Occurs at the junction where the right and left hepatic bile ducts meet.
- Distal Cholangiocarcinoma :- Occurs further down the bile duct near the small intestine.
Risk Factors :-
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) :- A chronic disease causing inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts.
- Chronic Liver Disease :- Such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.
- Bile Duct Abnormalities :- Congenital bile duct cysts or bile duct stones.
- Parasitic Infections :- Liver fluke infections in certain regions.
- Age :- Most common in people over 50.
- Family History :- A family history of bile duct cancer or other biliary diseases.
- Obesity and Diabetes :- Can increase the risk of bile duct cancer.
Symptoms :-
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Itching (pruritus)
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Fatigue
Diagnosis :-
- Blood Tests :- To check liver function and detect tumor markers (e.g., CA 19-9).
- Imaging Tests :- Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) to visualize the bile ducts.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) :- A procedure using an endoscope to examine the bile ducts and take biopsy samples.
- PTC (Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography) :- A procedure where contrast dye is injected into the bile ducts to take X-ray images.
- Biopsy :- Removing a small tissue sample for microscopic examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment :-
- Surgery :- The main treatment for early-stage bile duct cancer, often involving the removal of part of the liver, bile ducts, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Liver Transplant :- In some cases, for intrahepatic or perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.
- Radiation Therapy :- Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells, often used after surgery.
- Chemotherapy :- Using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing, can be used before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant), and for advanced stages.
- Targeted Therapy :- Drugs that target specific abnormalities in cancer cells.
- Palliative Care :- Focused on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life, especially in advanced stages.
Prognosis :-
- The prognosis for bile duct cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed and the location of the tumor. Early-stage cancers that can be surgically removed have a better prognosis, but overall, bile duct cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, leading to a poorer prognosis.
Prevention :-
- Manage Risk Factors :- Control liver diseases, avoid exposure to liver flukes, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Regular Check-ups :- For individuals with risk factors like PSC or a family history of bile duct cancer.
- Healthy Lifestyle :- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Here Are
bile duct cancer F&Q's
Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare cancer that starts in the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine.
Risk factors include primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), chronic liver disease, bile duct abnormalities, parasitic infections, age, family history, obesity, and diabetes.
Symptoms include jaundice, itching, dark urine, pale stools, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, fever, and fatigue.
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI, MRCP), ERCP, PTC, and biopsy.
Treatments include surgery, liver transplant, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and palliative care.
Recovery varies based on the specific procedure and individual patient factors. It may involve pain management, monitoring for complications, gradual resumption of diet and physical activity, and follow-up appointments to assess healing and adjust treatment as needed. Rehabilitation and support services may also be recommended to aid in recovery.







