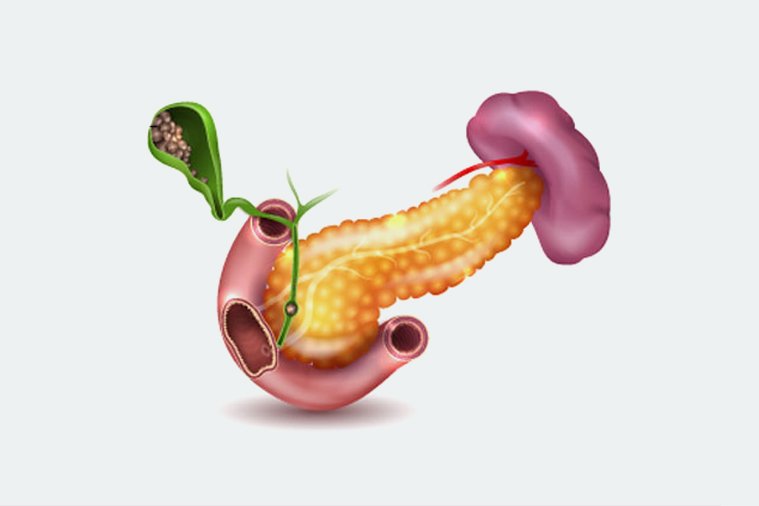
Gallbladder cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the gallbladder. It often goes undetected until it is in an advanced stage due to its asymptomatic nature in the early stages.
Types :-
- Adenocarcinoma :- The most common type, accounting for about 90% of gallbladder cancers, originating in the glandular cells lining the gallbladder.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma :- Originates in the flat cells lining the gallbladder.
- Adenosquamous Carcinoma :- Contains both glandular and squamous cells.
- Neuroendocrine Tumors :- Rare tumors originating from hormone-producing cells.
Risk Factors :-
- Gallstones :- The most significant risk factor.
- Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation :- Persistent inflammation can increase cancer risk.
- Age and Gender :- More common in older adults and women.
- Obesity :- Increases the risk of developing gallstones and gallbladder cancer.
- Family History :- A family history of gallbladder cancer or gallstones.
- Infection :- Chronic typhoid infection or other chronic infections.
- Abnormalities in the Bile Ducts :- Certain congenital bile duct abnormalities.
Symptoms :-
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right part of the abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Generalized itching (pruritus)
Diagnosis :-
- Imaging Tests :- Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and PET scans to visualize the gallbladder and surrounding structures.
- Blood Tests :- To check liver function and detect markers that may indicate cancer.
- Biopsy :- Removing a small tissue sample for examination under a microscope.
- Endoscopic Procedures :- ERCP or endoscopic ultrasound to get detailed images and possibly take biopsy samples.
Treatment :-
- Surgery :- The primary treatment for localized gallbladder cancer, often involving removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) and possibly parts of the liver and bile ducts.
- Radiation Therapy :- Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells, often used after surgery.
- Chemotherapy :- Using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing, which can be used before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant).
- Targeted Therapy :- Drugs that target specific abnormalities in cancer cells.
- Palliative Care :- Focused on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life, especially in advanced stages.
Prognosis :-
- The prognosis for gallbladder cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed. Early-stage gallbladder cancer has a better prognosis, but most cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage due to the lack of early symptoms.
Prevention :-
- Manage Risk Factors :- Maintain a healthy weight, avoid smoking, and manage chronic gallbladder inflammation.
- Regular Check-ups :- For those with risk factors, regular medical check-ups can help in early detection.
- Healthy Diet :- A diet high in fiber and low in fats can help reduce the risk of gallstones and gallbladder issues.
Here Are
Gallbladder Cancer F&Q's
Gallbladder cancer is a rare cancer that starts in the gallbladder, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to its asymptomatic nature in early stages.
Major risk factors include gallstones, chronic gallbladder inflammation, age, gender, obesity, family history, chronic infections, and bile duct abnormalities.
Symptoms include abdominal pain, jaundice, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, fever, dark urine, pale stools, and generalized itching.
Diagnosis involves imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI, PET scans), blood tests, biopsies, and endoscopic procedures like ERCP.
Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and palliative care.
The prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis. Early-stage cancer has a better prognosis, but most cases are diagnosed late.







