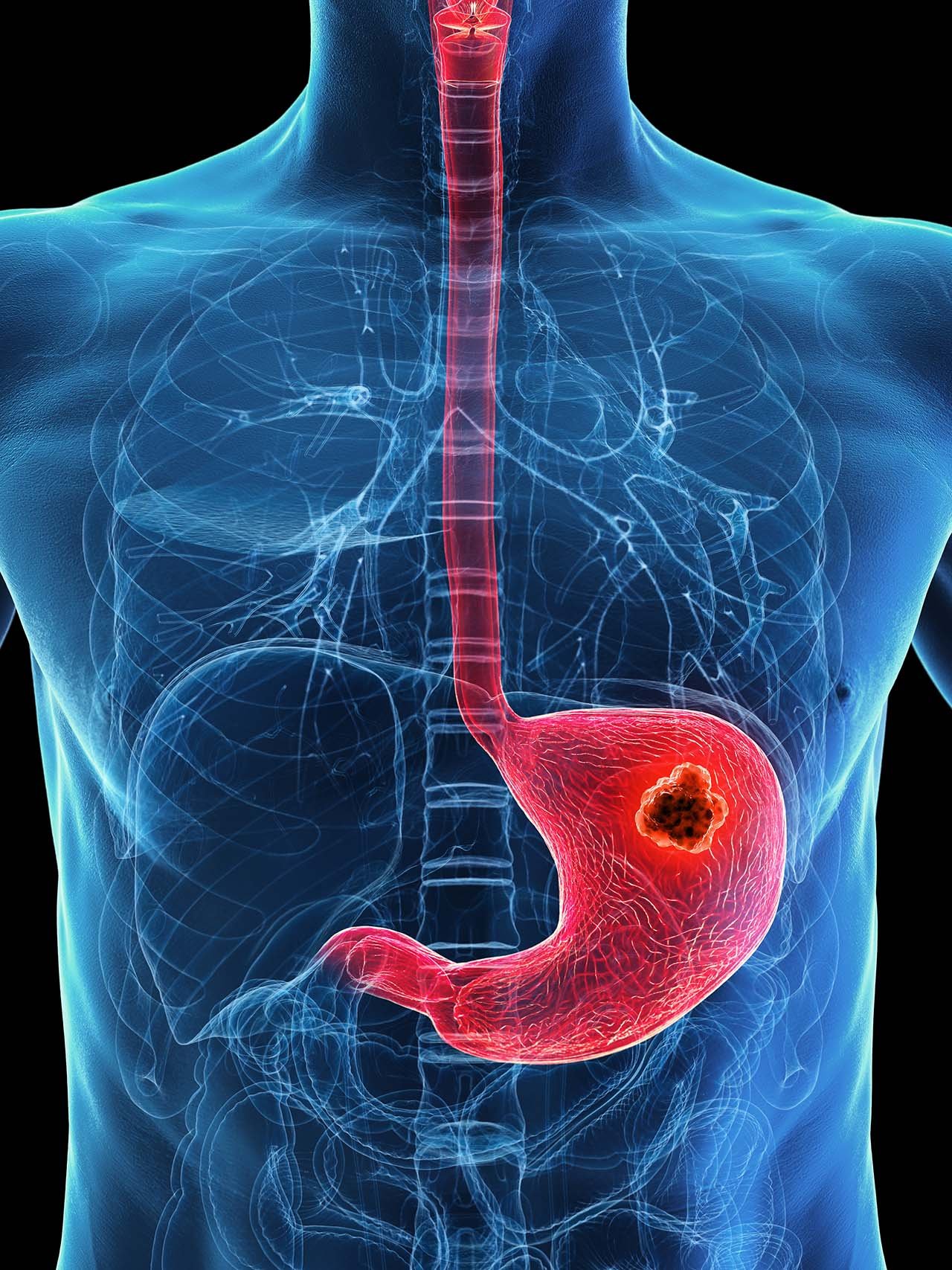
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is one of the most common and serious cancers affecting the digestive system. It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lining of the stomach, eventually forming a tumor. Early detection and timely treatment play a key role in improving survival and quality of life.
In this article, Dr. Sachin Arora, an experienced specialist in gastrointestinal health, explains the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment approaches for stomach cancer
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer develops when the cells in the inner lining of the stomach begin to grow abnormally. Over time, this growth can spread to other layers of the stomach wall, nearby lymph nodes, and even other organs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer:
H. Pylori Infection – Chronic infection with this bacteria is a major cause.
Unhealthy Diet – High intake of salty, smoked, or processed foods.
Smoking & Alcohol – Both increase cancer risk significantly.
Family History – Genetics can play a role.
Obesity – Linked to many cancers, including gastric cancer.
Previous Stomach Surgery or Ulcers – Increases risk in some individuals.
Common Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
Early-stage stomach cancer often has no obvious symptoms, making it difficult to detect. However, watch out for:
Persistent indigestion or heartburn
Loss of appetite
Unexplained weight loss
Nausea and vomiting (sometimes with blood)
Feeling full after eating small amounts
Stomach pain or discomfort
Fatigue and weakness
If these symptoms persist, it is important to consult a doctor without delay.
Diagnosis
Doctors may use several tests to diagnose stomach cancer, including:
Endoscopy – To view the inside of the stomach.
Biopsy – Tissue samples taken for examination.
Imaging Tests – CT scans, MRI, or PET scans.
Blood Tests – To check overall health and rule out other causes.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer, overall health, and other factors. Options may include:
Surgery – Removing part or all of the stomach (gastrectomy).
Chemotherapy – To kill or control cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy – Often combined with chemotherapy.
Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy – Modern treatments designed to attack cancer cells specifically.
Can Stomach Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all cases are preventable, certain lifestyle changes can reduce risk:
Eat a balanced diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables.
Avoid excessive salt, smoked, and processed foods.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Treat H. Pylori infection promptly if diagnosed.
Final Thoughts
Stomach cancer is a serious condition, but with early diagnosis and modern treatment methods, many patients are able to live longer, healthier lives.
Dr. Sachin Arora emphasizes the importance of paying attention to persistent digestive issues and seeking medical advice at the earliest. Awareness, timely check-ups, and a healthy lifestyle can make all the difference.